How to charge eneloops?
If you take care of them, they’ll take care of you
Select one of the following questions to find out how to charge your Eneloops.
Basic Eneloop charging questions
Is slow charging better than fast charging for Eneloops?
I think this is a very common mistake people make. They think that slow charging will result in longer cycle life. This is not true just by itself! They put their Eneloop Pros in a time-based charger and think they are treating their batteries nicely. Wrong.
Please look at the Tests Page for the 5000 cycles test. It is not mainly about the charge current but when the charge stops. Charging at a slow current can actually be more problematic when the charger can not detect whether a battery is full. At a higher charge rate, it is easier for the charger to detect a Voltage drop and Temperature increase and therefore know when to stop charging. These 2 checks can be missed when the batteries are charged at a low current! Not every charger terminates at a certain Voltage like the Powerex MH-C9000.
My quote for max cycle life: “It`s better to stop the charge prematurely using a high charge current than to overcharge with a low charge current.”
What do ma and mah stand for?
mA is the unit (mili Ampere) used for the charging current, which you can compare to “the speed of charging”. The higher the mA the faster Eneloop batteries will charge. mA is also used for the discharge current. Eneloop chargers generally charge between 150 and 1500mA depending on the charger.
mAh stands for milliAmpere hour. This refers to the amount of energy (capacity/charge) that a battery contains. On every Eneloop there is a mAh number written. This is the total capacity the battery can contain. A regular white Eneloop AA has a capacity of 1900mAh.
What is the difference between mA and mAh? And how do they work?
So how does it (not) work!
Let`s take a standard Eneloop with a capacity of 1900mAh. When you have a charger that uses a charge current of 100mA, the battery will be fully charged in 19 hours. 19 hours of 100mA = 19*100=1900mAh
This is a simplified way of looking at it, but not really the way mAh actually works.
Why not?
It`s the opposite:
To simplify it, you take a battery with 1900mAh and a device (let`s take a flashlight for example) that uses a low current of 100mA. The battery will take 19 hours to discharge the battery from 1900 till empty. So 19 hours of discharge at 100 mA equals 1900 mAh.
Isn`t that the same? Why can`t you use that with charging instead of discharging?
Let`s go back to the first example. A battery charger uses a charge current of 100mA. When you charge the battery for 19 hours you will have 1900mAh charged. This is also written on a standard Eneloop, so the 1900mAh of capacity is now inside the battery.
But
Now you extend the charge time to a total of 25 hours. This would imply that you do 25*100mA which would result in 2500mAh. This is the problem! A 1900mAh battery can only hold 1900 mAh even if you put 2500mA into it.
Still not sure?
Try to compare it with a 1-gallon jug. Fill the jug with 1 gallon of water and it`s full. When you continue throwing water into it, it will still only be 1 gallon of water inside the jug. When you empty the jug, only 1 gallon of water would come out. Simple.
This is a very basic way of looking at it. In real life, the mAh depends on a few more factors, like the discharge current that is being used, the age of the battery (how much it is used), and the (ambient) temperature.
How many times can Eneloop rechargeable batteries be recharged?
I believe they can be charged for hundreds of times, but under certain conditions. This includes a predefined amount of current for charging and discharging, an ambient temperature of X degrees, and a certain amount of rest within their amount of charge and discharge cycles.
I also believe that they can be charged more than 2100 times. It really depends on how you charge them, and how much you discharge them and at what current.
So that means that my Eneloop batteries can`t be charged 2100 times?
Hmm, most likely you won`t be able to do this. No need to feel upset. Imagine you would charge them twice every week for “just” 1000 times. We are then looking at 104 cycles in a year. In order to get 1000 cycles, you would be using those batteries for over 9 years. I believe that is quite a long time. Imagine how much environmental damage you would have saved by not using Alkaline batteries.
2100 cycles is just a marketing lie?
No, definitely not. It is according IEC and JIS testing specifications. A friend of mine, Viking (a member of the CPF forum) has helped me to understand these testings. The Japanese JIS 8708 Panasonic now uses is the same as the IEC 61951-2.
Sanyo and Panasonic didn’t make up some lousy numbers. They tested them according to these standards. The cycles are counted until there is 60% capacity left from the original capacity when the test stops. See the graph for the 2nd generation Eneloops that explains this a little.
See this image: https://eneloop101.com/wp-content/uploads/sh04_01.gif
Do Eneloop batteries need a special charger?
Not really. But it depends on what kind of charger you are talking about. I made a list of some of the best battery chargers for NiMH batteries, and they are great for Panasonic Eneloops as well.
However, not every brand and every charger will do a good job. The charger needs to be a ‘smart charger’ so it knows when to stop charging. Time-based chargers are not recommended at all!
But if you can’t afford a advanced charger like the one linked above, get a good Eneloop charger.
Do Eneloop Lite batteries need a special charger?
They can be charged in your average Eneloop charger unless the charge current is too high.
I recommend you double-check the charge current of your (Eneloop) charger. For AAA Eneloop Lite, the charge current shouldn’t be higher than 500mA. For AA (Lite), the charge current shouldn’t exceed 1000mA.
But.
You shouldn’t use these chargers for Eneloops:
Can I use my Duracell/Energeizer charger?
Eneloop batteries can generally be charged with any kind of NiMH battery charger. Duracell, Energizer and no-name. But to keep things simple, you better stay away from these 2 kinds of chargers:
Ultra fast chargers and Dumb chargers.
Ultra Fast chargers use a very high current to charge your batteries. This means that the current will exceed the maximum charge current advised by Panasonic by about 2-3+ times. Check the PDF product sheets for the fast charge currents on the Eneloop lineup page per battery model.
A side effect of charging at a high current is heat. One thing that NiMH LSD batteries in general don`t like is heat. Especially Eneloop PRO cells do not like to be charged hot. This will reduce their life cycle! 2 Examples of the 15-minute chargers which you should be staying away from or only need in a great emergency.

Dumb chargers charge batteries for a set amount of hours. Often they will only charge batteries in pairs. This is not recommended.
Eneloop lite AA have a minimum of 950 mAh, and Eneloop Pro AA have a minimum of 2500 mAh.
Imagine a charger charging at 100mA for 16 hours, this would exceed the capacity of the Eneloop lite. And not enough for filling up an Eneloop Pro. Fortunately, they use a rather low charge current and therefore won`t damage the batteries as much.
How long do Eneloop batteries hold a charge
Eneloop batteries can hold at least a charge for 10 years! There is a test on this website that shows a 10-year-old Sanyo Eneloop still having charge left after 10 years. Another discharge test can be found here: http://budgetlightforum.com/comment/1477075#comment-1477075 where the batteries in question were 12 years and 9 months old. Discharged right out of their package!
Eneloop PRO will lose a charge quicker, but still only 15% within 1 year.
Here’s the test I did with 10 year old Eneloop batteries.
https://youtu.be/ubcp8PHzUzY
What is the recommended charge current for Eneloops?
The recommended charge rate depends on the model and size. Have a look at all the product sheets on the overview page. There you will see the fast charge current. It`s better not to charge at a very low current because it is more difficult for the charger to recognize if a battery is full. My recommendations for manual chargers; (charge rate: 0.3C-1C). This is also the recommended charge rate by Maha / Powerex.
AA std= between 700mA and 2000mA
AA PRO= between 700mA and 2500mA
AA lite= between 300mA and 1000mA
AAA std= between 250 and 750mA
AAA PRO= between 300 and 1000mA
AAA lite= between 200 and 500mA
An Eneloop technician actually recommended charging with .5C – 1C. But if the charger is good enough, the lower charge current (about 1000mAh or lower ). Scroll down to understand what C means.
What’s the best Eneloop charger?
The short answer:
The best and most advanced Eneloop charger currently available is the Panasonic BQ-CC65. It is Panasonic’s flagship. Check out more info on the Panasonic BQ-CC65. Or check out where to buy it.
The long answer:
You can charge Eneloops with any NiMH charger. But not everything works well.
What you want is a smart analyzer charger.
Smart chargers can detect when a battery is fully charged and usually have a backup cut-off using a timer. (See the Advanced section for detailed information) This will limit charging-related damage to a minimum.
They also charge cells individually so you can remove or add another battery during charging. You can also mix AA and AAA batteries in the same charger as it will look at the individual bays.
The recommendeded simple smart chargers: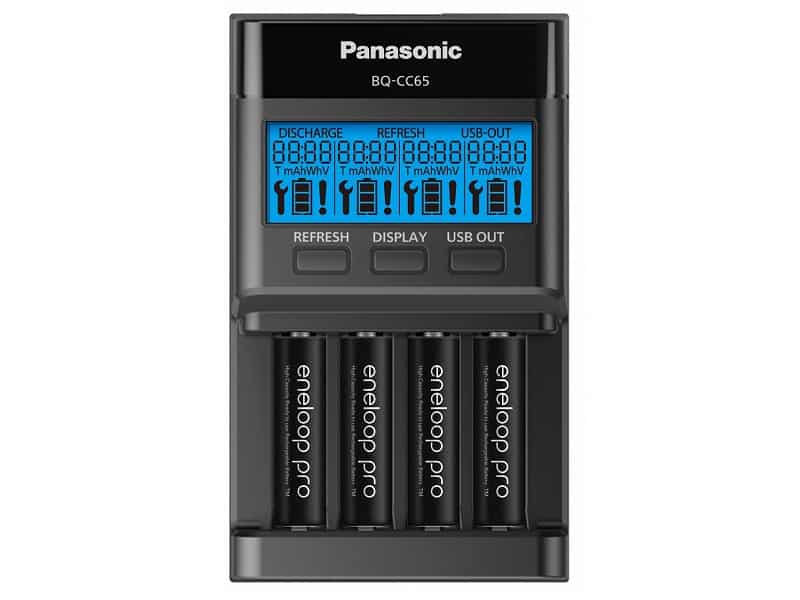
Are you new to rechargeable batteries? For a simple charger, I would currently recommend the Panasonic BQ CC65 for Eneloop standard and PRO. It will charge relatively fast and uses colored LED lights to show whether a battery is empty, still charging, fully charged, or damaged. This is great for people who don`t want to wait for a long time and want a clear indicator that batteries are charging, or full.
The Panasonic BQ CC17 is also used by many and is very affordable. But at the same time, it is quite a bit slower and older. If you don`t care about the charge speed this could be your option. Please look at the Eneloop battery charger overview page for more information on all chargers made by Sanyo and Panasonic.
If you are more of a geek take a look at intelligent analyzer chargers like the Powerex Maha MH C9000, Opus BT-3100/3400, SkyRC MC3000, and the like. These chargers can refresh your batteries, and check the capacity! More about this is in the Best AA battery chargers section.
Eneloop voltage?
The normal resting voltage for Eneloops is somewhere between 1.2V and 1.4V. During use, the average voltage is about 1.2 Volts.
So, why does my Eneloop charger stop charging at 1.6 Volts and sometimes at 1.45 V?
What is the maximum charging voltage for Eneloop?
That is normal behavior. It depends on the battery you charge, the charge speed, and how old/often it is used. But the ambient temperature also influences this a lot. If you charge a battery in a very cold room, your end Voltage will be higher than in a warm room. Also, keep in mind that the voltage will drop after it finished charging, so you usually don’t see the highest voltage unless you test it directly after the charge.
Please take a look at this graph below that is taken from a 4th generation Eneloop standard product sheet. You will see quite a difference in Voltage in relation to Ambient temperature.
The blue line almost reaches 1.7V when the ambient temperature is around 0 degrees Celsius. Many chargers have a cut-off voltage at around 1.65V.
When the temperature is 40 degrees Celsius, the end-voltage is much lower at around 1.55V.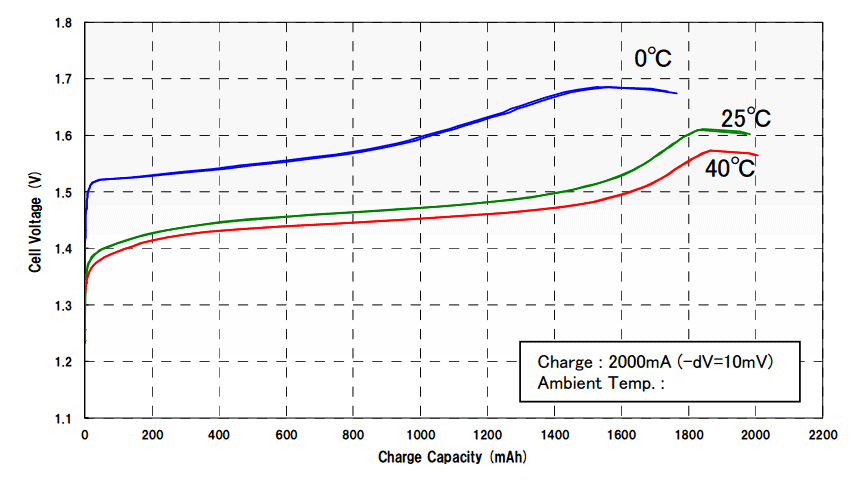
Can you overcharge Eneloop batteries?
Yes, unfortunately, you can definitely overcharge Eneloop batteries. This is possible when you use a dumb charger (time-based charger). The charger will continue supplying a charging current for X number of hours. The battery charger will only stop when the timer has run out.
Another way is by trickle charging.
The most common problem is with using DECT phones that stand on a charging cradle most of the day. These charging devices provide a very low charge current to keep the batteries charged. The problem however is that Eneloop batteries don’t like this type of charging.
For Eneloop PRO batteries it is even disastrous because this will reduce their cycle life tremendously. This is because they are much more prone to heat and overcharging.
Do I need to charge my new Eneloop batteries before I start using them?
No, that is not necessary. The package claims it: Ready to use, and that is correct. This means you can use the Eneloop batteries right out of the package. Just keep in mind that Eneloops do not come fully charged from the factory. They are charged about 70% when leaving the factory, and before they are in your hands.
I did a test with a brand new (old stock) but 10-year-old Eneloops, and the batteries still held a 60% charge. So only if you want to use their full capacity you should charge them before using them.
Should I discharge my Eneloops completely before charging them?
No, that is unnecessary.
Actually, you could extend battery life by not fully discharging them. The same goes for fully charging your batteries each time. But generally speaking, you don’t need to worry too much about using Eneloop batteries and Eneloop chargers. Just make sure you don’t use a dumb charger. They will charge the batteries for x amount of hours, and eventually, kill the battery.
How long does it take for Eneloop to charge?
Generally speaking, it takes between 1.5 hours and 12 hours, depending on the number of batteries you charge simultaneously.
Here’s an overview of how fast each battery charger charges at maximum speed. Most battery charges will charge slower the more batteries are added! The charge time usually doubles when you go from charging 2 batteries to charging 4 batteries.
Panasonic BQ-CC17 | AA: 7 hours | AAA: 5 hours
Panasonic BQ-CC55 | AA: 1.5 hours | AAA: 1.5 hours
Panasonic BQ-CC57 | AA: 2 hours | AAA: 1.5 hours
Panasonic BQ-CC65 | AA: 1.5 hours | AAA: 1.5 hours
How to refresh your Eneloops
Give them a cup of water or even a lollypop. Joking aside, you can do a refresh with the built-in Refresh function on some Panasonic and Sanyo Eneloop chargers (Panasonic BQ-CC65).
With a Refresh mode, the charger will charge, discharge, and then do a final charge to complete the cycle. This will normally boost the capacity back to its maximum possible capacity. You can use this method with all NiMH batteries, not just Eneloops. This is a very handy feature when reviving older / often used batteries! I usually recommend doing a refresh once or twice a year when you don`t use your Eneloops often.
BTW you can repeat this Refresh mode if you’re not satisfied with the results of the 1st Refresh cycle. Some advanced chargers will continue this cycle until the max capacity is reached. So the continuation of the process may depend on the charger.
Some Panasonic and Sanyo chargers have a built-in refresh function. This goes automatically, but you can’t really see whether the capacity has increased or not. The reason to do a Refresh is because the batteries have either been used a lot, or not so much at all. With a refresh you can maximize their capacity again.
I recommend using an advanced charger like the ones I mentioned in the Best Battery Chargers list. You can set your own parameters, and decide which charge currents and discharge currents you want.
It is recommended to set a refresh at between 1000-2000mA for the charge rate and 500-1000 mA for the discharge rate, for regular (white) AA Eneloops with a capacity of 1900mAh or 2000mAh.
Pro Tip! Some chargers like the Lacrosse BT C700 and Voltcraft IPC 1L have problems with refreshing Eneloop PRO batteries when set at 200 mA charge. It’s better to set the charge rate at max, in this case, 700mA.
But don’t go over 2000mAh for AA Eneloops.
Can I refresh Eneloops if I don’t have a charger with a refresh option?
Yes, you could. Just charge them up with the charger you have, and put them in an old-fashioned flashlight with an incandescent bulb, run it until they’re completely dead, then charge them up again. Repeat this about 2 or 3 times in a row.
You better use a flashlight with an incandescent bulb because most modern LED flashlights have different built-in digital power circuitry which will all work differently and probably quit working before the batteries are completely discharged. Therefore don’t use an LED flashlight for this, unless you know how much current it draws.
When to use the Analyze / Refresh mode with Eneloops?
When you want to know the capacity, or when you want to give them a little boost. It can be very useful to match batteries for multi-cell applications. You check which Eneloops have the closest capacity and use those in an application to protect the batteries from an over-discharge / deep discharge.
How many years do Eneloops last?
There are numerous people who have been using Eneloops for 10-15 years without too much trouble. But those are usually the standard edition with 1900mAh capacity.
Eneloop PRO, on the other hand, die sooner and you could probably use them for 5 years or so if they are not abused.
It really depends on how much you take care of the batteries. If you don’t discharge them below 0.9V and don’t discharge them at extreme currents, you could use them for a very long time.
My recommendation is to get standard Eneloops with 1900mAh or 2000mAh, which can be used for many years, as they are one of the toughest rechargeable batteries on the planet.
You can see a thread on Budgetlightforum where people shared how long they have been using their Eneloops: https://budgetlightforum.com/t/how-are-your-oldest-eneloops-doing/25648/35
buy Eneloops here
Check out the Eneloop seller’s page for the best deals on authentic Eneloops. Check out the counterfeit Eneloops page if you decide to buy from an unkown source or from eBay, AliExpress, Lazada, Shopee etc.
Advanced Eneloop Charging information
What is battery C rate?
C = equal to (full) capacity. If the capacity of the battery is 2000 mAh and you charge at 1C it will be 1* the capacity of 2000= 2000mA. This means the charge will take 1 hour to charge the battery. If you see a .5C it means half of the capacity so in this case the half of 2000 = 1000. So at half the charge rate, it`s taking 2 hours to fill.
Another way to remember it is to say, 0.5C is 0.5 times the capacity. 0.1C is 0.1 times the capacity.
A little help: Try to see 1C as 100% charge current.
0.5C is going to be 50% = 2 hours
0.2C is going to be 20% = 5 hours
0.1C is going to be 10% = 10 hours
0.05C is going to be 5% = 20 hours
The recommended C-rate for Eneloops is .5C to 1C. This means a charge current of 1000-2000mA for normal Eneloop AA batteries.
What is -dV/dt charging ? (termination)
This is a charge termination method that detects a full battery when the Voltage of the battery drops within a certain time during the charge.
– means negative
d means delta/change
V means Voltage
t means time.
Delta can be translated as a Change. So if the charger senses a change in voltage so that the Voltage drops (which means negative) within X amount of time it knows the battery is fully charged. See this graph that HKJ made and look at the Red line. Just before it stops charging you can see it going down. The charger that uses a -dV/dt algorithm detects the battery is fully charged and terminates the charge.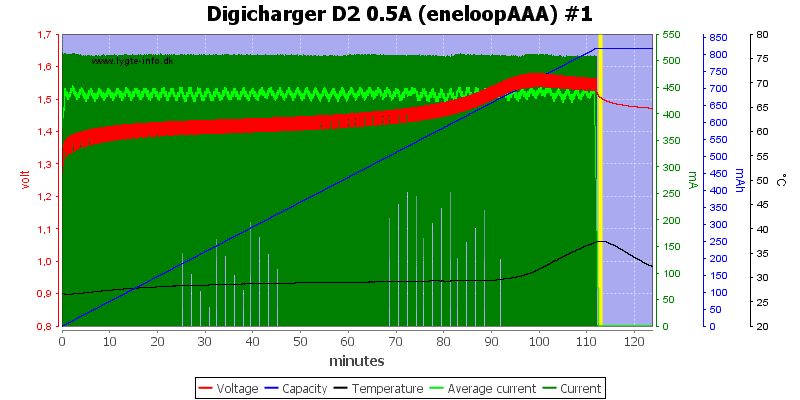
The problem with low C charge rates is that the Voltage drop is difficult to measure. Therefore it is better to use a .5C or 1C rate when using this algorithm. Also notice that the black line, and temperature rises at the same time, they go hand in hand.
What is 0 dV/dt termination?
Instead of measuring whether a Voltage drops, like the aforementioned -dV/dt termination, this one does it in a different way.
When a battery is depleted the Voltage is lower than when fully charged. When you charge a battery, the Voltage will rise over time. But at a certain Voltage, the battery stops increasing its Voltage, and therefore the charger could determine to stop charging. The 0 dV refers to 0 Voltage difference at x amount of time. As the battery tester, HKJ, has pointed out, this type of termination is sometimes difficult to distinguish from a -dV/dt termination.
A charger like the Lacrosse BC700 probably uses this termination, especially at a lower current.
This is not a recommended termination for NiMH rechargeable batteries, and therefore neither for Eneloop batteries.
What is CC/CV charging?
CC= constant current
CV= constant voltage
This algorithm will charge a battery with a constant current that stays until the Constant Voltage is reached. This is used with charging Lithium-Ion batteries for example, so Panasonic NiMH chargers do not have this charge algorithm. Take a look at the following graph by HKJ.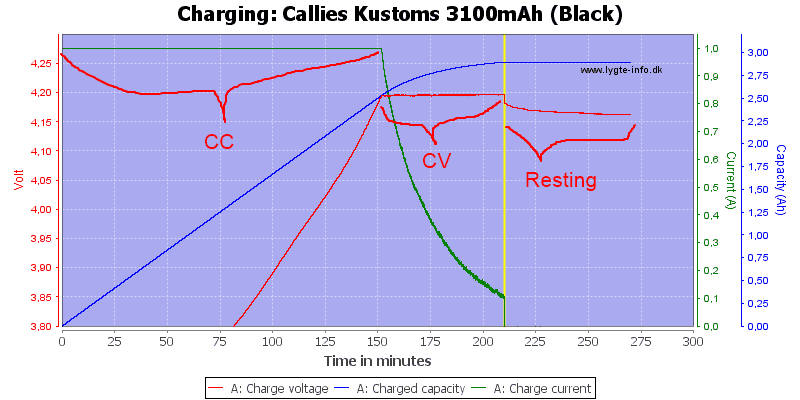
Although constant current is used often for a longer period, they usually slow down when the battery is almost full.
What is a trickle charge?
Trickle charge is usually referred to as keeping a battery on the charger at a very low charge current. This is meant to keep the battery as full as possible over an extended period of time.
NiMH battery chargers don`t usually include this feature. Some chargers like the Panasonic BQ-CC16 and BQ-CC55 use a 1-hour trickle charge to top off the battery. It might even be the wrong terminology as it is a fairly high Trickle charge and sometimes people call it a top-off charge. The BQ-CC17 on the other hand does not use this topping off. Likely because it uses a lower current, to begin with.
Panasonic Eneloop batteries don’t like to be continuously charged via trickle charging. This will reduce the battery life significantly. Eneloop PRO batteries can die within months if the batteries are continuously charged via trickle charging.
What is a break-in? Do Eneloops need a break-in?
No, this has nothing to do with burglars or with your breakfast. But a Break-In for batteries is referred to as maximizing the performance or capacity of a battery. (However, this is different from a Refresh or Analyze mode)
The Maha Powerex MH -C9000 for example has a Break-In option.
Warning: A break-in cycle should always start with an empty battery.
The charger will charge for 16 hours 0.1C charge rate, then rest for an hour, do a 0.2C discharge, rest again, and at the end again charge for 16 hours at 0.1C according.
(I don`t know to what Voltage the Powerex will discharge, but according to the IEC standards, section 7.1 it should be 1V.)
If you do an Analyze or Discharge, you should be able to know the capacity, do NOT look at the “charge capacity” during the Break-In!
When to use a break-in with Eneloops?
Only with an empty battery! When using rechargeable NiMH batteries people advise doing a Break-In right out of the package. I personally don`t think you need to do this with Eneloops. It`s a great feature for old rechargeable AA or AAA batteries that are almost useless or completely dead.
My advice would be to not use the Break-In mode (too often) with Eneloops, especially not with Eneloop Pro. Eneloops don`t really need it unless you want to have the extra 5+% capacity.
Ps. New Eneloop batteries need a few cycles to get to max capacity… (This is also written in each battery product specification.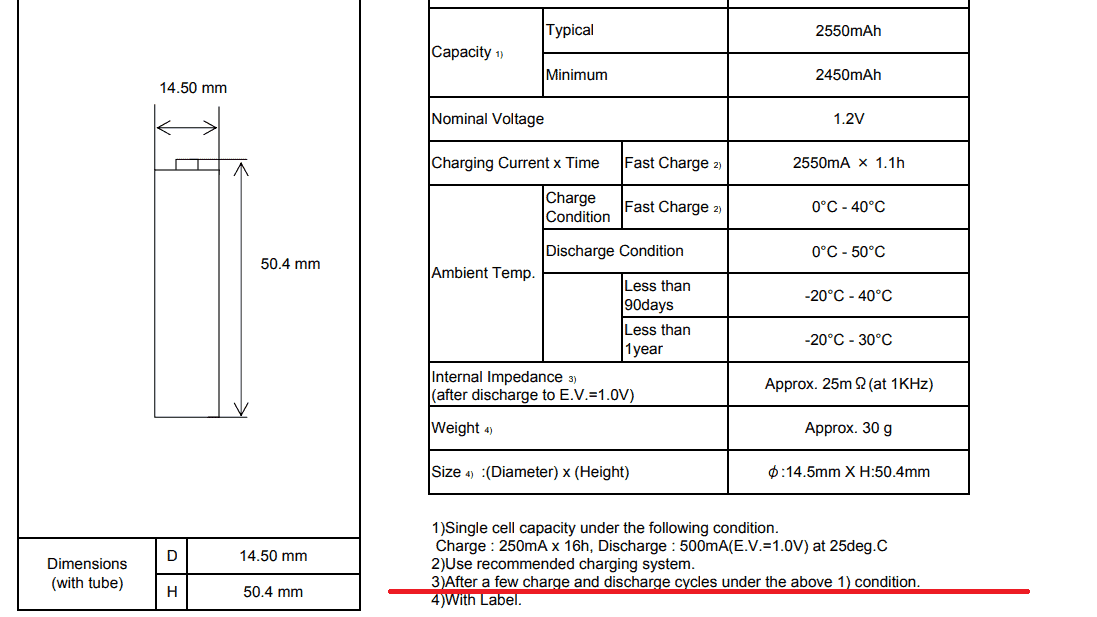
What is an over-discharge?
This is a common problem when using batteries in a multi-battery application. Say for example a flashlight that uses 4 AA batteries in series. When 1 battery is charged for 50% and the other 3 to 100%, and you use the flashlight, the batteries will drain and the 50% charged battery will be empty before the others and the current keeps flowing through the battery which will damage this battery and increase its internal resistance.
It is therefore always advised to use sets of batteries always together, and the Eneloop limited editions will greatly help to keep track of your sets.
I asked some Eneloop engineers, who said that over-discharge is much worse than overcharge.
Over-discharge starts at 0.8V, and at around 0.6V damage will occur.
How is the cycle life tested for Eneloops? (IEC61951)
This is rather technical. But every trustworthy battery manufacturer that uses these IEC or JIS standards has to follow these rules:
Test conditions:
1 Before the battery cycle test is done the battery has to be discharged at a Constant Current of 0.2C which is 380mA for a standard model Eneloop battery.
2 The battery cycle test has to be carried out at a room temperature of 20 degrees Celsius +-5 degrees
3 The battery should not rise above 35 degrees during the test. If so the battery should be cooled down by forced air draught.
Battery cycle testing is done in sets of 50 cycles, with the following requirements:
Cycle 1: charge at 0.1C for 16 hours. Start discharge directly after the charge has finished, without a break at 0.25C for 2 hours and 20 minutes
Cycle 2-48: charge at 0.25C for 3 hours and 10 minutes. Start discharge directly after the charge has finished, without a break at 0.25C for 2 hours and 20 minutes.
Cycle 49: charge at 0.25C for 3 hours and 10 minutes. Start discharge directly after the charge has finished, without a break to 1.0V
Cycle 50: charge at 0.1C for 16 hours. Rest for 1-4 hours. And discharge at 0.2C to 1V.
If cell drops below 1.0V during the 1-48th, the discharge may be terminated.
After the Discharge of every 50th cycle, it is allowed to stop the cycle test until a later time before continuing with the 51st cycle. This is also allowed at the 100th, 150th, 200th, 250th, etc. cycle.
When does the test stop?
When the duration of the 50th discharge cycle becomes less than 3 hours, the discharge test has to be redone according to the specification of the 50th cycle. When both of these cycles have a smaller discharge duration of 3 hours the test is considered complete.
At this stage, the battery can only provide 60% of its capacity. So the cycle test stops at the 60% mark.
See the picture above.
Where do you get the 60% from?
In the Advanced section at the bottom of this page, I explain what the C-rate means.
Imagine a full battery to be 100%. If we discharge a battery at 20% speed of the full capacity it should take 5 hours to empty. Because 5 times 20% equals 100%.
Please understand this before you proceed with reading.
Well, you can compare 0.2C discharge rate with 20%. (see the Discharge Rate during the 50th cycle).
If the 50th discharge cycle ends within 3 hours instead of 5 hours you can calculate the %.
If 100% discharge takes 5 hours, then how much percent will 3 hours be?
Yep, 60%.
Conclusion:
The life cycle test will stop when the battery can`t reach 60% of its original capacity during a 50th cycle-set. (the cycle tests are done in sets of 50 charges and discharges as can be read here above).
These are the FAQ questions about charging Eneloops. If you want to see other questions, not related to charging, check out the Eneloop FAQ page.